
The natural history of children with severe combined immunodeficiency: baseline features of the first fifty patients of the primary immune deficiency treatment consortium prospective study 6901. Human severe combined immunodeficiency: genetic, phenotypic, and functional diversity in one hundred eight infants. doi: 10.1007/s1087-1.īuckley RH, Schiff RI, Schiff SE, Markert ML, Williams LW, Harville TO, et al. Clinical characteristics and genetic profiles of 44 patients with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID): report from Shanghai, China (2004–2011) J Clin Immunol.

Yao C, Han X, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Jin Y, Cao R, et al. Adapting the screening algorithm for pre-term/ill infants reduces the amount of false positive test results. The TREC cut-off score determines the percentage of non-SCID TCL cases detected in newborn screening for TCL. The sensitivity of TREC based NBS for typical SCID was 100 %. Individual TREC contents in all SCID patients was <25 TRECs/μl (except in those evaluated with the New York State assay). PPV within the five largest cohorts was 0.8-11.2% for SCID and 18.3-81.0% for TCL. In the prospective cohort studies, SCID incidence was ~1.7:100,000, re-test rate was 0.20-3.26%, repeat DBS rate 0.0-0.41% and referral rate 0.01-1.35%. In case series, the sensitivity for typical SCID was 100%.
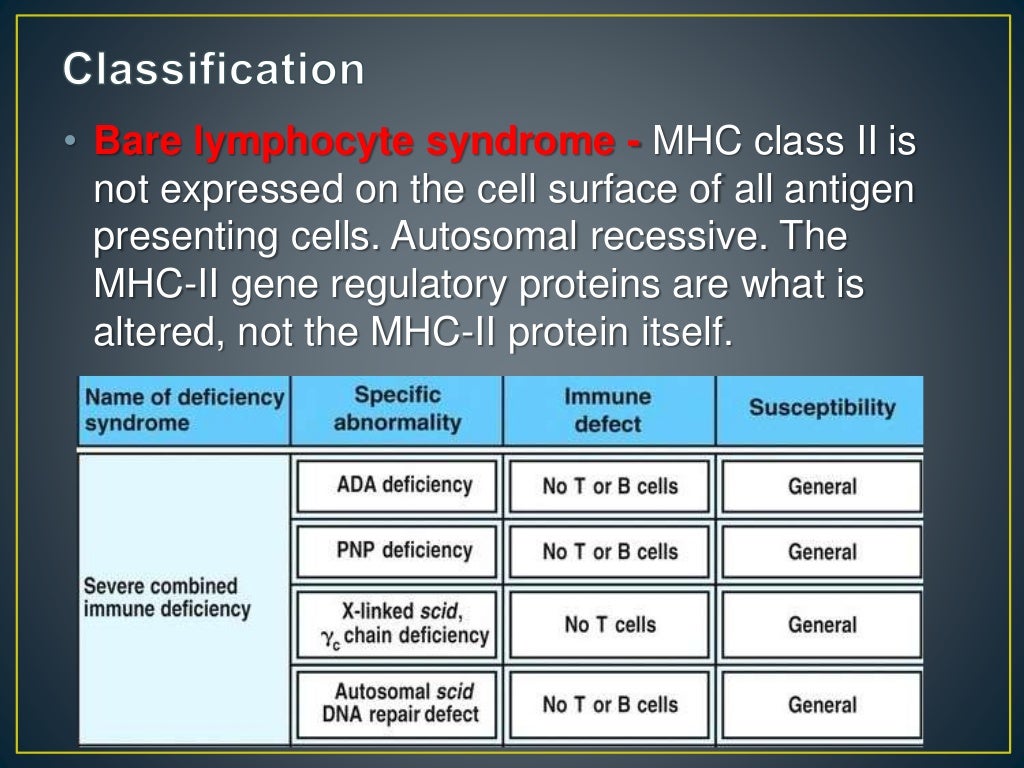
Severe combined immunodeficiency disease scid series#
Thirteen studies were included, re-confirming 89 known SCID cases in case series and reporting 53 new SCID cases in 3.15 million newborns. We calculated positive predictive value (PPV), test sensitivity and SCID incidence. We extracted TREC content and cut-off values, number of retests, repeat DBS and referrals, and type and number of typical SCID and other T cell lymphopenia (TCL) cases. PubMed, EMBASE and the Cochrane Library were systematically searched for case series and prospective cohort studies describing TREC based NBS for SCID. To systematically review the diagnostic performance of published algorithms for TREC based NBS for SCID. In recent years, different screening algorithms for TREC based SCID screening were reported. Newborn screening (NBS) by quantifying T cell receptor excision circles (TRECs) in neonatal dried blood spots (DBS) enables early diagnosis of severe combined immunodeficiency disease (SCID).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
